Definitions
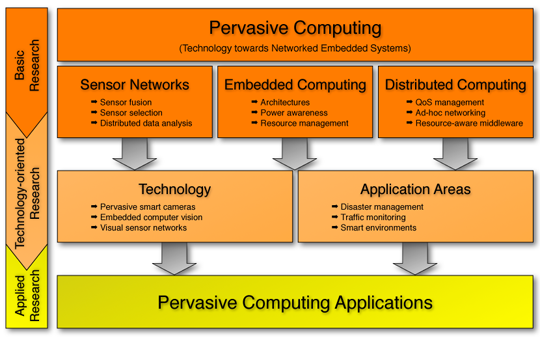
Pervasive computing
·
The idea
that technology is moving beyond the personal computer to everyday devices with
embedded technology and connectivity as computing devices become progressively
smaller and more powerful.
·
Also
called ubiquitous computing,
pervasive computing is the result of computer technology advancing at
exponential speeds -- a trend toward all man-made and some natural products
having hardware and software.
The
devices are getting a lot smaller and a lot more powerful.
Ubiquitous computing
·
A post-desktop model of
human-computer interaction in which information processing has been thoroughly
integrated into everyday objects and activities.
·
Ubiquitous technology is often wireless, mobile, and networked,
making its users more connected
to the world around them and the people in it.
This
diagram shows what the user can do on the move as more people use their mobile
phones for most applications today. Such as communicating (text, phone, calls
and emails), they are also used for gaming.

Ambient computing
·
Electronic environments that
is sensitive and responsive to the presence of people.
·
As these devices grow
smaller, more connected and more integrated into our environment, the
technology disappears into our surroundings until only the user interface
remains perceivable by users.
Disappearing
computing
·
A
vision of the future is one in which our world of everyday objects and places
becomes infused and augmented with information processing and exchange.
·
Disappearing
computing is technology evolving to become a part of our life without us
noticing. Such as computer tables and TVs embedded into our walls and speakers
under the floor etc.
Pervasive
computing is also known as ubiquitous computing so they are very similar.
Pervasive computing talks about how device are getting smaller.
No comments:
Post a Comment